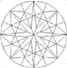
Diamond Cutting
Diamond Shapes
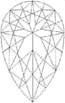
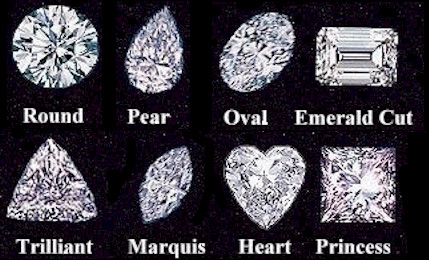
An uncut, unpolished diamond resembles a large crystal taken from the ashes of a fire. The diamond cutter decides the final shape for the cut stone. Some possible shapes (top and side views shown) are these:
|
|
 |
 |
 |
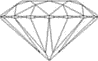 |
|||
| Round Brilliant Cut |
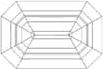
Emerald Cut |
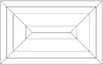
Baguette Cut |
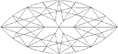
Marquise Cut |
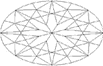 |
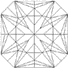 |
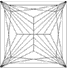 |
 |
| Oval Cut |
Flanders Cut |
Princess Cut |
Pear Cut |
Diamond Cutting
Diamonds can be cleaved or sawn. Cleaving takes a few seconds but it must be done with the grain or the stone will break roughly and be ruined.
Most diamonds are sawn. In the sawing process, a bronze blade impregnated with diamond dust spins at high speed to gradually cut through the stone. To saw through a one-carat diamond might take eight hours. Diamonds can also be cut with a laser. After cleaving or sawing is complete, the faceting takes place.
Faceting
Faceting — cutting planes or faces onto the surface of the stone — is done with most transparent gemstones. The purpose is to let light pass through and be reflected and refracted from faces on the back of the stone. Faceted cuts are precisely designed to show off the gem to best advantage. The diagram shows the facets of a round stone.
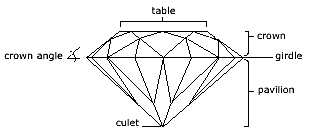
For a discussion of the importance of good proportions in a faceted diamond, see The 4 Cs of Diamonds: Cut Proportions.
In faceting a diamond, waste is unavoidable. The average weight loss is about 50% percent, though more or less of the rough may be lost based on cutting proportions. Poorly proportioned stones retain more weight while the best proportions require greater loss of weight. Diamond price can vary as much as 50% between two stones, equal in all respects except cut proportions.


A poorly proportioned diamond is like a steak with the fat left on.
A well cut diamond is like a delicious filet.
Where diamonds are cut
Major cutting industries are in:
- Antwerp and Tel Aviv, where many of the fancy shapes — pear shaped, marquise, etc. — are cut;
- New York City, where many of the larger (3-10 carat) diamonds are cut;
- Bombay, where, because of low labor costs, most smaller and lower quality stones are cut; and
- Russia, which specializes in cutting stones from its own mines, which produce much of the world's higher-valued rough diamond.